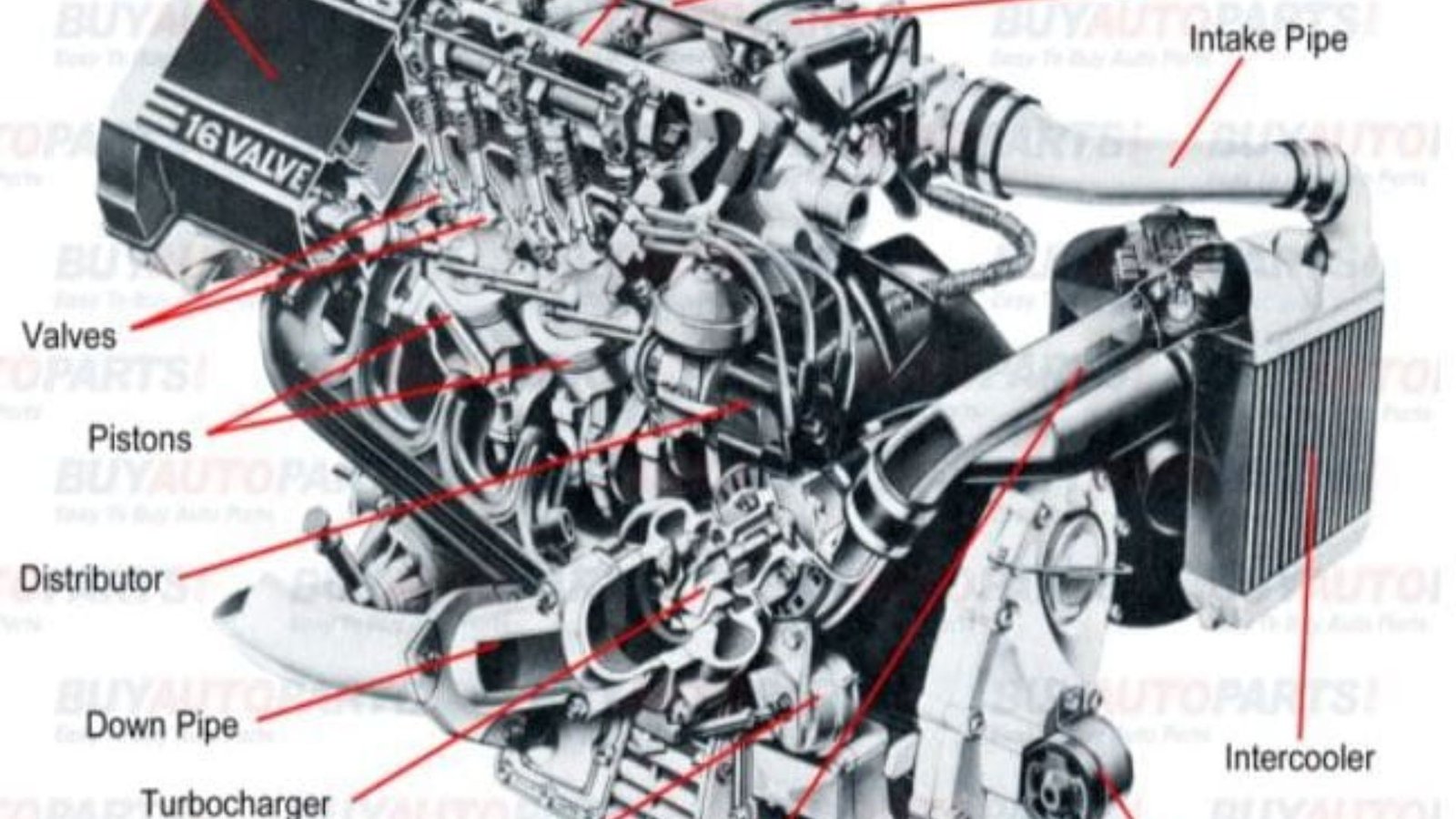
An engine is a complex machine with many crucial parts working together to power your vehicle. Understanding these parts and how they function can help you better appreciate your vehicle’s performance and maintenance needs. Here’s a breakdown of the essential parts of an engine and their roles.
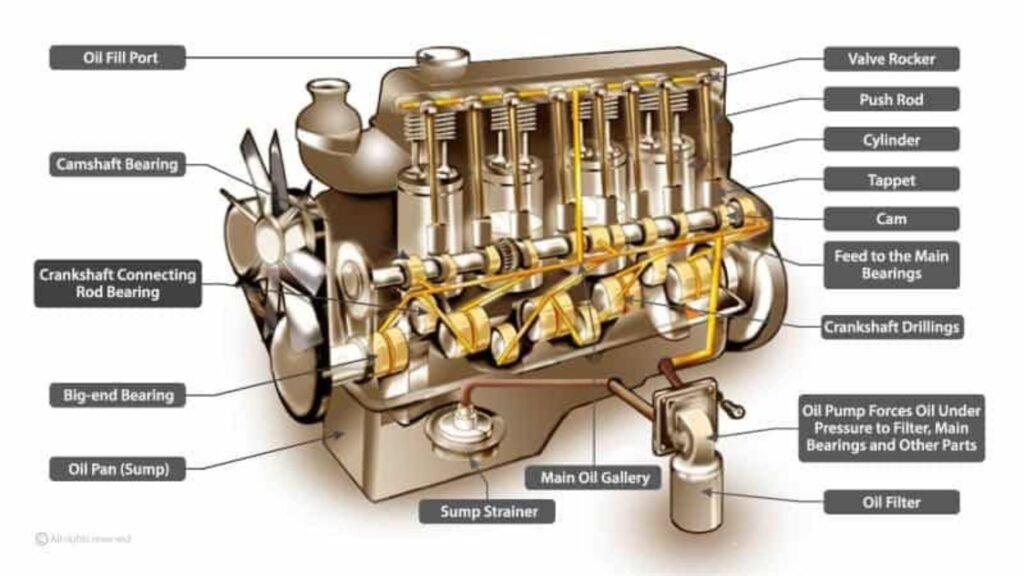
1. Cylinders
1.1 Function and Design
Overview: Cylinders are the core components where the engine’s power is generated through the combustion process.
Key Points:
- Combustion Chambers: Each cylinder contains a combustion chamber where fuel and air mix and ignite.
- Arrangement: Engines can have different cylinder configurations, such as inline, V-shaped, or flat.
Benefits:
- Power Generation: Cylinders are essential for creating the power needed to move your vehicle.
Drawbacks:
- Complexity: More cylinders can lead to a larger and heavier engine.
2. Pistons
2.1 Purpose and Operation
Overview: Pistons move up and down within the cylinders to transfer energy from combustion to mechanical motion.
How They Work:
- Movement: Pistons are driven by the force of combustion, pushing them down the cylinder and turning the crankshaft.
- Seals: They are equipped with piston rings to seal the combustion chamber and prevent leaks.
Benefits:
- Energy Transfer: Convert the energy from combustion into mechanical motion.
Drawbacks:
- Wear and Tear: Pistons and rings can wear out over time and require maintenance.
3. Crankshaft
3.1 Role and Mechanism
Overview: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion that drives the vehicle.
How It Works:
- Rotation: As pistons move up and down, they turn the crankshaft, which then transmits this rotational force to the transmission and wheels.
- Balancing: The crankshaft is balanced to reduce vibrations and ensure smooth operation.
Benefits:
- Power Transmission: Essential for converting piston movement into usable power.
Drawbacks:
- Complexity: Requires precise balancing and alignment.
4. Camshaft
4.1 Function and Operation
Overview: The camshaft controls the timing of the opening and closing of the engine’s valves.
How It Works:
- Valve Timing: The camshaft has lobes that push on the valve lifters, opening and closing the valves at the correct times.
- Synchronization: It is synchronized with the crankshaft via a timing belt or chain.
Benefits:
- Efficient Airflow: Ensures optimal airflow into and out of the cylinders for efficient combustion.
Drawbacks:
- Maintenance: Requires proper timing and maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
5. Valves
5.1 Types and Functions
Overview: Valves regulate the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the engine.
Types:
- Intake Valves: Allow air and fuel to enter the combustion chamber.
- Exhaust Valves: Allow exhaust gases to exit the combustion chamber.
Benefits:
- Controlled Combustion: Essential for efficient engine operation and performance.
Drawbacks:
- Wear: Valves can wear out or become damaged over time.
6. Timing Belt/Chain
6.1 Purpose and Mechanism
Overview: The timing belt or chain ensures that the camshaft and crankshaft remain in sync, allowing the engine’s valves to open and close at the correct times.
How It Works:
- Synchronization: Connects the crankshaft to the camshaft, maintaining precise timing.
- Material: Timing belts are usually made of rubber with reinforced fibers, while chains are metal.
Benefits:
- Accurate Timing: Ensures that engine components operate in harmony for efficient performance.
Drawbacks:
- Replacement: Timing belts need to be replaced periodically, and a timing chain, though more durable, can still stretch over time.
7. Fuel Injectors
7.1 Function and Operation
Overview: Fuel injectors spray a precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber, mixing it with air for ignition.
How They Work:
- Injection: Fuel injectors are controlled electronically to deliver the right amount of fuel at the right time.
- Efficiency: Ensures proper fuel-air mixture for efficient combustion.
Benefits:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Provides accurate fuel delivery for better performance and fuel economy.
Drawbacks:
- Clogging: Fuel injectors can become clogged or dirty, affecting performance.
8. Spark Plugs
8.1 Purpose and Operation
Overview: Spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber with a spark.
How They Work:
- Ignition: Generate an electric spark to ignite the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing combustion.
- Maintenance: Should be checked and replaced periodically to ensure proper engine performance.
Benefits:
- Reliable Ignition: Essential for starting and running the engine smoothly.
Drawbacks:
- Wear and Tear: Spark plugs can wear out over time and require replacement.
9. Oil Pump
9.1 Role and Operation
Overview: The oil pump circulates engine oil to lubricate and cool the engine’s moving parts.
How It Works:
- Circulation: Pumps oil from the oil pan through the engine, ensuring all moving parts are properly lubricated.
- Pressure: Maintains adequate oil pressure for effective lubrication.
Benefits:
- Engine Longevity: Prevents excessive wear and overheating by providing necessary lubrication.
Drawbacks:
- Maintenance: Requires regular oil changes to maintain proper function.
10. Radiator
10.1 Purpose and Function
Overview: The radiator helps to cool the engine by dissipating heat from the engine coolant.
How It Works:
- Cooling: Coolant flows through the radiator, where it releases heat to the outside air.
- Efficiency: Ensures the engine operates within a safe temperature range.
Benefits:
- Prevent Overheating: Essential for maintaining optimal engine temperature and performance.
Drawbacks:
- Maintenance: Requires regular checks for leaks and blockages.
Conclusion
Each part of an engine plays a crucial role in its operation and performance. From the cylinders and pistons to the fuel injectors and spark plugs, understanding how these components work together can help you better maintain your vehicle and appreciate the technology that powers your ride. Regular maintenance and attention to these essential parts ensure your engine remains in top condition, delivering reliable performance and efficiency.