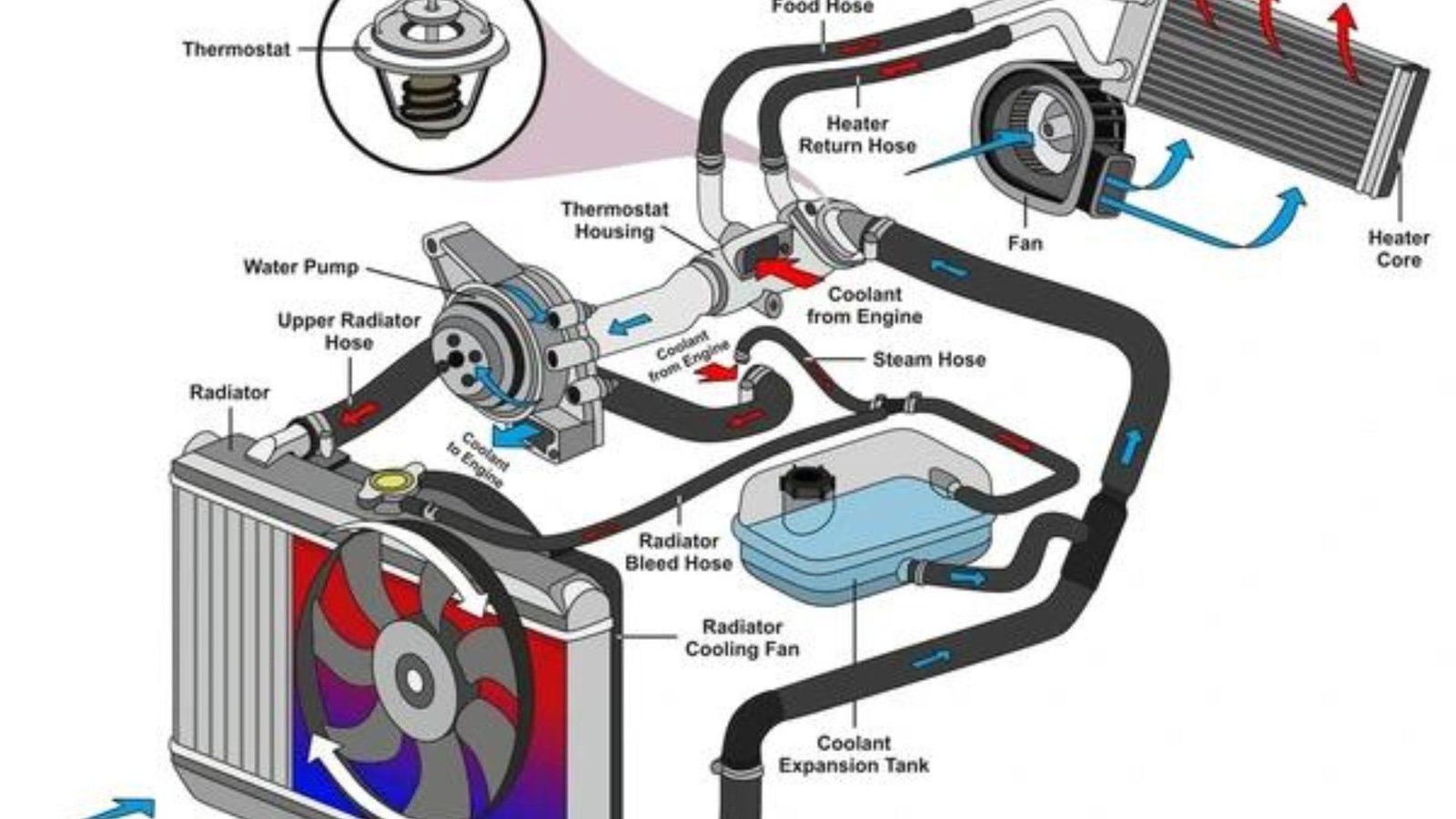
Engine cooling systems are essential for maintaining optimal engine temperature and ensuring reliable performance. These systems prevent overheating, which can cause serious engine damage and reduce efficiency. Understanding how engine cooling systems work, their components, and how to maintain them is key to keeping your vehicle in top condition. Here’s what you need to know.
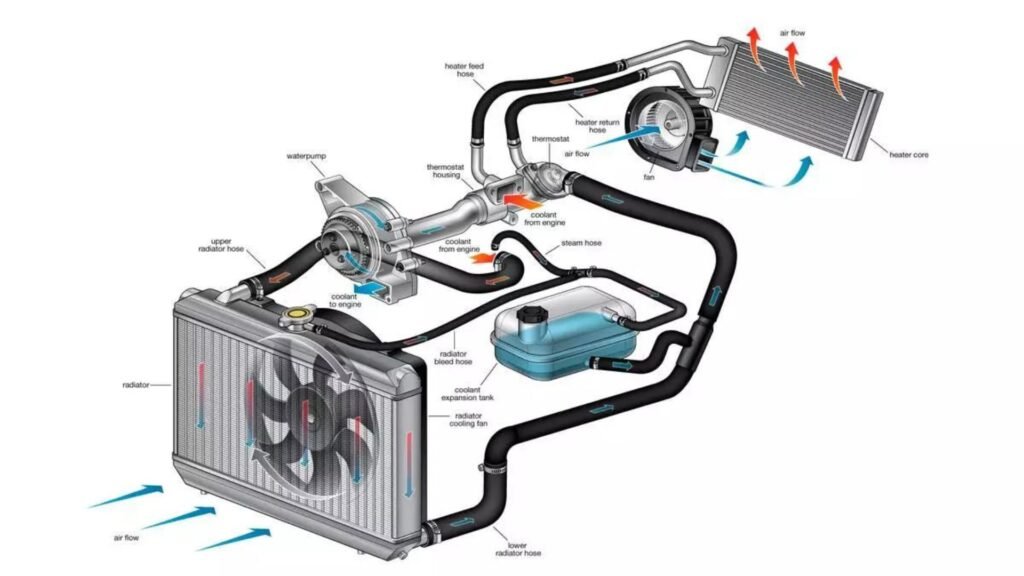
1. Understanding Engine Cooling Systems
1.1 The Purpose of Engine Cooling
Overview: The primary function of an engine cooling system is to regulate the engine’s temperature. An engine generates a lot of heat during operation, and if this heat isn’t managed properly, it can lead to overheating and potential damage.
Key Functions:
- Heat Dissipation: Moves excess heat away from the engine.
- Temperature Regulation: Keeps the engine operating within its optimal temperature range.
Importance:
- Prevents Overheating: Avoids engine damage and maintains performance.
- Ensures Longevity: Helps extend the life of engine components.
2. Types of Engine Cooling Systems
2.1 Liquid Cooling System
Overview: Liquid cooling systems use coolant (a mixture of water and antifreeze) to absorb and transfer heat away from the engine.
Components:
- Radiator: Cools the heated coolant by transferring heat to the air.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine and radiator.
- Thermostat: Regulates the temperature by controlling coolant flow.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores extra coolant and allows for expansion.
Benefits:
- Efficient Cooling: Provides effective heat management.
- Temperature Control: Maintains consistent engine temperature.
Maintenance Tips:
- Check Coolant Levels: Ensure the coolant is at the proper level.
- Inspect for Leaks: Regularly check for leaks in the radiator, hoses, and connections.
- Flush Radiator: Periodically flush the radiator to remove debris and old coolant.
2.2 Air Cooling System
Overview: Air cooling systems use air to dissipate heat from the engine. This method is typically found in older vehicles and motorcycles.
Components:
- Cooling Fins: Metal fins on the engine block or cylinder head increase surface area for heat dissipation.
- Fan: Moves air across the cooling fins to enhance cooling.
Benefits:
- Simplicity: Fewer parts compared to liquid cooling systems.
- Less Maintenance: No need for coolant changes.
Maintenance Tips:
- Inspect Cooling Fins: Ensure fins are free of debris and in good condition.
- Check Fan Operation: Verify that the fan is working properly.
3. Cooling System Components and Their Functions
3.1 Radiator
Overview: The radiator is the central component of the liquid cooling system. It dissipates heat from the coolant into the air.
Functions:
- Heat Exchange: Transfers heat from the coolant to the air.
- Coolant Flow: Allows coolant to flow through the engine and radiator.
Maintenance Tips:
- Check for Blockages: Ensure the radiator is not obstructed by debris.
- Inspect for Leaks: Look for signs of leakage or corrosion.
3.2 Water Pump
Overview: The water pump circulates coolant through the engine and radiator.
Functions:
- Circulation: Keeps coolant moving to ensure effective heat transfer.
- Pressure Maintenance: Maintains proper pressure in the cooling system.
Maintenance Tips:
- Listen for Noise: Unusual noises can indicate a failing water pump.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect for leaks around the water pump area.
3.3 Thermostat
Overview: The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature.
Functions:
- Temperature Control: Opens and closes to maintain engine temperature.
- Flow Regulation: Controls coolant flow to the radiator.
Maintenance Tips:
- Monitor Temperature: Ensure the engine reaches and maintains the proper operating temperature.
- Replace as Needed: Replace a faulty thermostat to prevent overheating.
3.4 Coolant Reservoir
Overview: The coolant reservoir holds excess coolant and allows for expansion.
Functions:
- Storage: Provides additional coolant for the system.
- Expansion: Accommodates coolant expansion as it heats up.
Maintenance Tips:
- Check Levels: Ensure the reservoir has adequate coolant.
- Inspect for Cracks: Look for cracks or damage in the reservoir.
4. Signs of Cooling System Problems
4.1 Overheating Engine
Overview: An overheating engine is a common sign of cooling system issues.
Symptoms:
- High Temperature Gauge: Temperature gauge reads higher than normal.
- Steam or Smoke: Visible steam or smoke from the engine.
Possible Causes:
- Low Coolant Levels: Insufficient coolant can cause overheating.
- Cooling System Leaks: Leaks can lead to coolant loss and overheating.
Solutions:
- Add Coolant: Top up coolant levels if low.
- Inspect for Leaks: Repair any leaks in the system.
4.2 Coolant Leaks
Overview: Coolant leaks can lead to low coolant levels and overheating.
Symptoms:
- Puddles Under Vehicle: Coolant leaks are often visible as puddles or spots.
- Low Coolant Warning: Dashboard warning light indicating low coolant levels.
Possible Causes:
- Damaged Hoses: Cracked or damaged hoses can cause leaks.
- Faulty Radiator: Leaks in the radiator can result in coolant loss.
Solutions:
- Repair Hoses: Replace damaged or cracked hoses.
- Fix Radiator Leaks: Repair or replace a leaking radiator.
4.3 Reduced Heater Performance
Overview: Poor heater performance can indicate a problem with the cooling system.
Symptoms:
- Cold Air from Heater: Heater blows cold air instead of warm.
- Inconsistent Temperature: Fluctuating heater temperature.
Possible Causes:
- Low Coolant Levels: Insufficient coolant can affect heater performance.
- Thermostat Issues: A faulty thermostat can disrupt heater operation.
Solutions:
- Check Coolant Levels: Ensure coolant levels are adequate.
- Replace Thermostat: Replace a malfunctioning thermostat.
5. Regular Maintenance and Inspection
5.1 Importance of Maintenance
Overview: Regular maintenance of the cooling system is crucial for preventing problems and ensuring efficient operation.
Maintenance Tasks:
- Regular Coolant Checks: Monitor and maintain proper coolant levels.
- Inspect Components: Regularly check for leaks, damage, or wear in cooling system components.
- Flush System: Periodically flush the cooling system to remove debris and old coolant.
Benefits:
- Prevents Overheating: Regular maintenance helps avoid overheating and engine damage.
- Improves Efficiency: Keeps the cooling system functioning optimally.
Consequences of Neglect:
- Increased Risk of Failure: Higher likelihood of engine overheating and damage.
- Higher Repair Costs: Neglect can lead to more severe and costly repairs.
Conclusion
Understanding and maintaining your vehicle’s cooling system is essential for optimal engine performance and longevity. Whether it’s a liquid cooling system or an air cooling system, each component plays a crucial role in managing engine temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring smooth operation. Regular checks, timely repairs, and proper maintenance can help you avoid common cooling system problems and keep your engine running efficiently. By staying informed and proactive, you can enhance your vehicle’s performance and avoid costly repairs.